Low-Temperature Plasma Surgical Electrode: A Precise and Safe Choice for ENT Surgery
In the field of medical surgical instruments, electrosurgical technology has become a core component of operating rooms with its vital role. Among various technologies, the low - temperature plasma surgical electrode is leading a transformation in surgical techniques with its unique advantages.
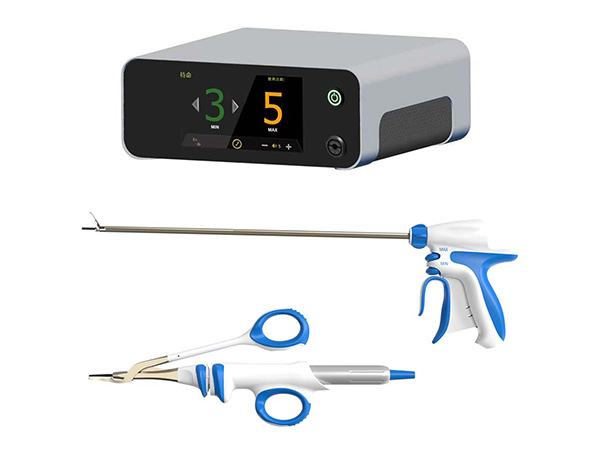
I. How the Low - Temperature Plasma Surgical Electrode Works
Using radio frequency electric field effects, the low - temperature plasma surgical electrode activates sodium ions in saline or electrolyte solutions. This creates a layer of ionized plasma between the two poles of the electrode. These highly active particles can efficiently break tissue bonds, enabling precise cutting and ablation. As the plasma's effect is extremely localized (within 100 microns), it only affects the tissue surface in contact with the electrode, avoiding deep tissue damage. Also, since the electric field is confined between the two poles, the electrode can operate at low temperatures (40 - 70℃). This greatly reduces the risk of heat damage and can even promote collagen shrinkage for hemostasis during ablation.
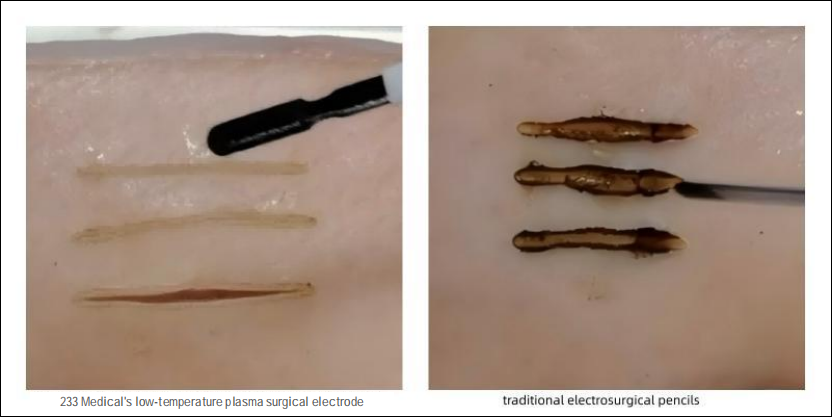
II. Technical Advantages
Outstanding Safety
Operating at low temperatures prevents heat - induced tissue burns. The minimally invasive approach reduces damage to healthy tissue.
Efficiency and Minimally Invasive
Minimal to no bleeding during surgery, no skin incisions means no scars. Patients can recover in just 2 - 3 days, achieving efficient treatment.

III. Applications in ENT Surgery
Tonsillectomy
Traditional tonsillectomy methods cause much bleeding and post - op pain. While electro knives and lasers reduce bleeding, their high temperatures can burn tissues. The low - temperature plasma surgical electrode offers precise cutting and simultaneous hemostasis. Operating at low temperatures reduces surrounding tissue damage, shortens surgery time, and lessens bleeding and pain.
Adenoidectomy
Adenoid curettage often has unclear surgical views, residual adenoids, and injury risks. Although adenoidectomy with a microdebrider under an endoscope is more thorough, bleeding remains a problem. The low - temperature plasma surgical electrode provides a clear view and precise targeting. It can cut and coagulate blood alternately, avoiding residual adenoids and significantly reducing intra - operative bleeding.
Inferior Turbinate Reduction
For chronic hypertrophic rhinitis, the low - temperature plasma surgical electrode performs submucosal puncture ablation of the turbinate. Through radiofrequency plasma energy, it forms scars and reduces nasal resistance. Its built - in dual - electrode technology prevents skin burns and current injuries. Acting only around the electrode needle in the interstitial layer, it preserves the mucosal surface and epithelium. This meets nasal physiological requirements and results in mild post - op edema.
The low - temperature plasma surgical electrode, with its precision, safety, and efficiency, is bringing new hope to ENT surgeries. It improves surgical outcomes and speeds up patient recovery, setting new standards in the field of ENT surgery.
Reference
233 Medical. (2025). Low-Temperature Plasma Surgical Electrode: ENT clinical application guidelines.
International Electrotechnical Commission. (2023). *IEC 60601-2-2: Medical electrical equipment – Part 2-2: Particular requirements for the basic safety and essential performance of high-frequency surgical equipment*.
Wang, X., et al. (2024). Low-temperature plasma versus radiofrequency in thyroid surgery: A multicenter RCT. Head & Neck, 46(3), 412–421.