LigaSure vs. Ultrasonic Scalpel: A Comparative Analysis
In the operating room, the selection of surgical energy devices is critical for optimal outcomes. Two leading technologies, the Ligasure vessel sealing system and the Ultrasonic scalpel, each offer distinct advantages for modern surgical procedures.
Ligasure: The Intelligent Vessel Sealing System
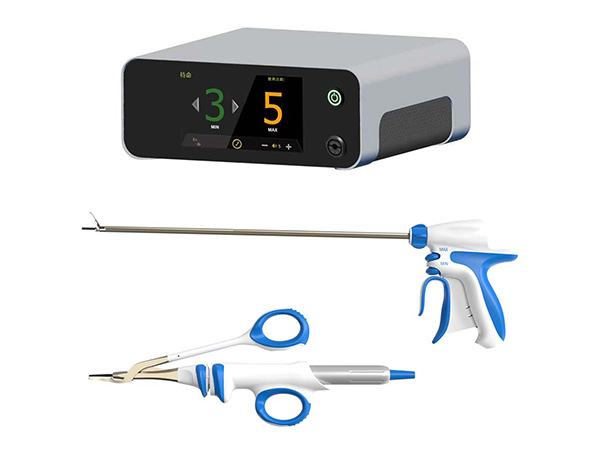
The Ligasure system represents an advanced bipolar electrosurgical platform. It functions as a feedback-controlled, intelligent bipolar device paired with an integrated cutting blade. Operating at a lower voltage than traditional systems, its design features a larger blade contact area to facilitate effective current delivery.
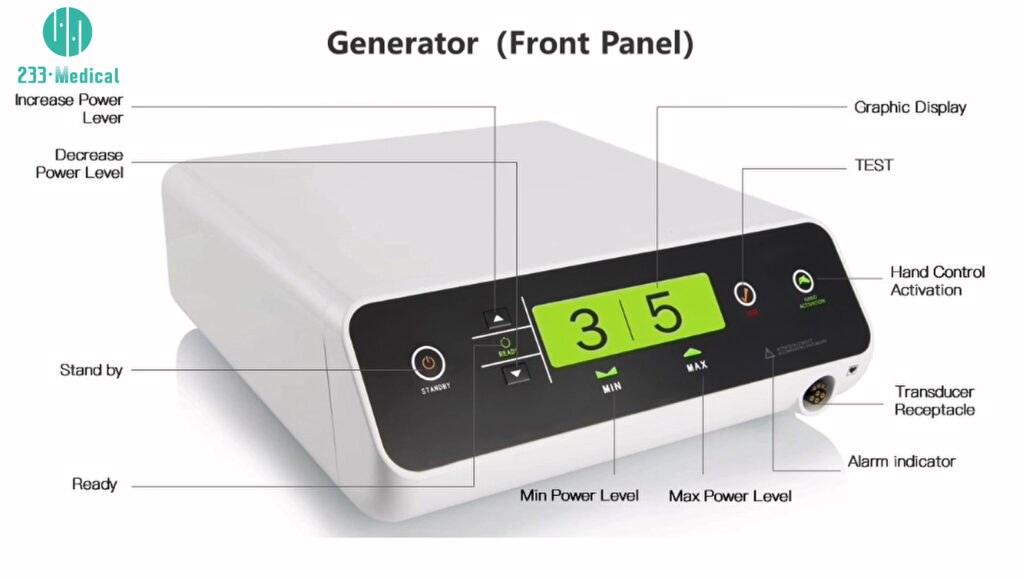
The system's core technology involves a smart generator that continuously monitors the electrical impedance of the tissue grasped between the instrument jaws. Once optimal fusion is achieved, the generator automatically deactivates the energy and provides an audible signal. This process delivers high-frequency current combined with mechanical pressure, denaturing the collagen and elastin within the vessel walls to create a permanent, translucent seal.
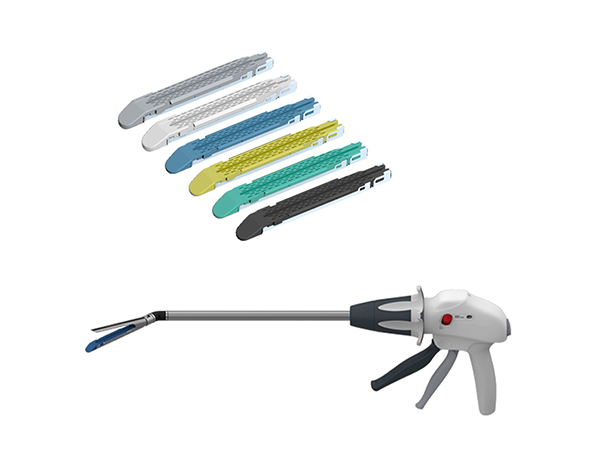
A key feature is the integrated cutting mechanism, which allows the surgeon to transect the sealed tissue without exchanging instruments. Documented benefits of the Ligasure system include:
- Effective sealing of vessels up to 7 mm in diameter (theoretical maximum).
- Ability to seal vessels within tissue bundles with minimal dissection.
- Creation of a seal capable of withstanding significantly elevated systolic pressures.
- Rapid sealing with minimal smoke production, preserving visual clarity.
- Reduced charring and odor, leaving no foreign material such as sutures or clips.
- Limited thermal spread, typically between 1.5 to 2.0 mm, minimizing collateral tissue damage.
This system is particularly suited for both laparoscopic and open oncologic surgeries, where it aims to enhance procedural safety. For optimal use, it is recommended to grasp an appropriate tissue volume (approximately 1/2 to 3/4 of the jaw length). Specific structures, like the infundibulopelvic ligament, may benefit from a double-sealing technique before transection. As with all surgical tools, technique must be adapted to the individual patient's anatomy and condition.
Ultrasonic Scalpel: Precision Ultrasonic Dissection
The Ultrasonic scalpel utilizes ultrasonic energy. Its transducer converts electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical vibrations, which are transmitted to the metal blade tip. This results in microscopic longitudinal vibrations (on the order of 50-100 μm).
This rapid oscillation generates frictional heat and produces localized stress that facilitates cleavage. The energy causes cellular water to vaporize and breaks protein hydrogen bonds, leading to protein denaturation, which simultaneously coagulates and divides tissue.
Its application in laparoscopic surgery offers several demonstrated advantages: significantly less lateral thermal injury compared to conventional electrosurgery, enabling precise dissection near vital structures. The reduction in smoke and eschar maintains a clearer operative field, potentially shortening procedure time. As no electrical current passes through the patient, it may enhance safety and contribute to reduced complication rates in certain procedures.
Conclusion
Both Ligasure and the Ultrasonic scalpel are cornerstone technologies in contemporary operative suites. Their distinct mechanisms—one based on advanced bipolar feedback and the other on ultrasonic vibration—provide surgeons with versatile, reliable options for hemostasis and dissection, allowing for tailored approaches to improve surgical precision and patient care.